A roof structure is part of an building envelope. It is the covering on the uppermost part of your building or shelter which gives protection from family pets and weather, rain or snow notably, but heat also, sunlight and wind. The term denotes the framing or structure which supports that covering also.[1]The characteristics of a roof are centered upon the goal of the building so it covers, the available roof covering materials and the local traditions of engineering and wider concepts of architectural design and practice and may also be governed by local or national legislation. In most countries a roof protects mostly against rain. A verandah may be roofed with material that protects against sunlight but admits the other elements. The roof of your garden conservatory protects plants from cold, wind, and rain, but admits light.

Shack manufactured from date hand branches at Neot Semadar, IsraelA rooftop may also provide additional living space, for example a roof covering garden.The elements in the look of a roof structure are:the materialthe constructionthe durabilityThe material of any roof may range between banana leaves, wheaten straw or seagrass to laminated cup, copper (see: copper roofing), aluminium sheeting and pre-cast cement. In many parts of the planet ceramic tiles have been the predominant roofing materials for centuries, if not millennia. Other roof covering materials include asphalt, coal tar pitch, EPDM silicone, Hypalon, reboundable foam, PVC, slate, Teflon textile, TPO, and lumber shakes and shingles.

The construction of an roof depends upon its method of support and the way the underneath space is bridged and set up roofing is pitched. The pitch is the viewpoint of which the roof goes up from its most affordable to highest point. Most US home structures, except in very dry regions, has roofs that are sloped, or pitched. Although modern construction elements such as drainpipes may remove the need for pitch, roofs are pitched for reasons of looks and custom. So the pitch is dependent after stylistic factors partly, and partially to do with practicalities.

Some types of roofer, for example thatch, need a steep pitch in order to be durable and waterproof. Other types of roofing, for example pantiles, are unstable over a steeply pitched roof but provide excellent weather protection at a relatively low angle. In regions where there is little rainfall, an almost even roof with hook run-off provides adequate protection against an intermittent downpour. Drainpipes remove the need for a sloping roofing also.

A person that specializes in roof covering construction is named a roofer.The durability of an roof structure is a matter of concern because the roofing is often the least accessible part of any building for purposes of repair and renewal, while its destruction or damage can have serious results.

Because the reason for a roof covering is to safeguard people and their possessions from climatic elements, the insulating properties of the roof are a concern in its composition and the choice of roofing material.Some roof materials, those of natural fibrous materials specifically, such as thatch, have excellent insulating properties. For those that not, extra insulation is often installed under the outside level. In developed countries, nearly all dwellings have a ceiling installed under the structural members of the roof. The goal of a ceiling is to insulate against heat and cold, noise, dirt and often from the lice and droppings of wild birds who frequently choose roofs as nesting places.

Cement tiles can be utilized as insulation. When installed going out of a space between the tiles and the rooftop surface, it can reduce heating system caused by the sun.Forms of insulation are plastic or sensed sheeting, with a reflective surface sometimes, installed directly below the tiles or other materials; synthetic foam batting laid above the ceiling and recycled paper products and other such materials that can be inserted or sprayed into roof cavities. So called Cool roofs have become popular significantly, and sometimes are mandated by local codes. Cool roofs are thought as roofs with both high reflectivity and high thermal emittance.

Poorly covered and ventilated roofing can suffer from problems such as the formation of glaciers dams throughout the overhanging eaves in winter, causing drinking water from melted snow on upper parts of the roof covering to permeate the roofing materials. Ice dams take place when warmth escapes through the uppermost part of the roof, and the snow at those true things melts, refreezing as it drips over the shingles, and collecting in the form of ice at the low points. This may cause structural damage from stress, including the devastation of gutter and drainage systems.
Pin 24in Span on Pinterest

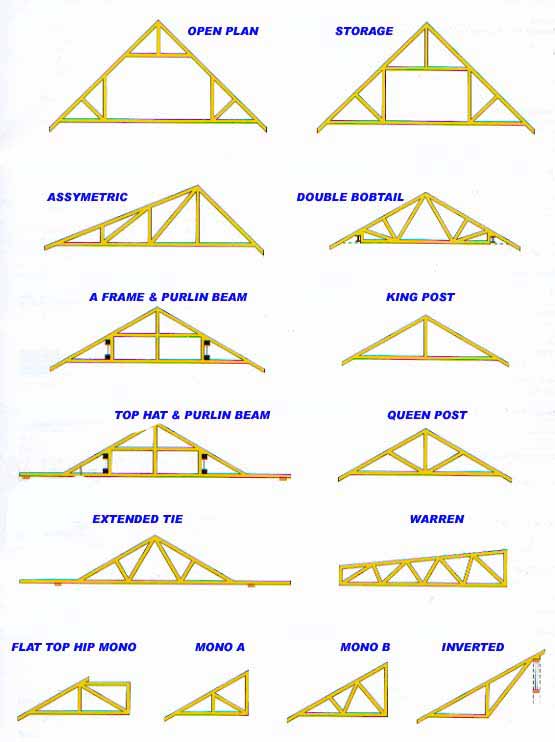
gambrel roof pole barn truss design gambrel shed roof truss calculator

Pin 24in Span on Pinterest

gambrel roof pole barn truss design gambrel shed roof truss calculator

Thanks a lot for reading and visit our blog, don't forget to share this informative article.
 A roof structure is part of an building envelope. It is the covering on the uppermost part of your building or shelter which gives protection from family pets and weather, rain or snow notably, but heat also, sunlight and wind. The term denotes the framing or structure which supports that covering also.[1]The characteristics of a roof are centered upon the goal of the building so it covers, the available roof covering materials and the local traditions of engineering and wider concepts of architectural design and practice and may also be governed by local or national legislation. In most countries a roof protects mostly against rain. A verandah may be roofed with material that protects against sunlight but admits the other elements. The roof of your garden conservatory protects plants from cold, wind, and rain, but admits light.
A roof structure is part of an building envelope. It is the covering on the uppermost part of your building or shelter which gives protection from family pets and weather, rain or snow notably, but heat also, sunlight and wind. The term denotes the framing or structure which supports that covering also.[1]The characteristics of a roof are centered upon the goal of the building so it covers, the available roof covering materials and the local traditions of engineering and wider concepts of architectural design and practice and may also be governed by local or national legislation. In most countries a roof protects mostly against rain. A verandah may be roofed with material that protects against sunlight but admits the other elements. The roof of your garden conservatory protects plants from cold, wind, and rain, but admits light. Because the reason for a roof covering is to safeguard people and their possessions from climatic elements, the insulating properties of the roof are a concern in its composition and the choice of roofing material.Some roof materials, those of natural fibrous materials specifically, such as thatch, have excellent insulating properties. For those that not, extra insulation is often installed under the outside level. In developed countries, nearly all dwellings have a ceiling installed under the structural members of the roof. The goal of a ceiling is to insulate against heat and cold, noise, dirt and often from the lice and droppings of wild birds who frequently choose roofs as nesting places.
Because the reason for a roof covering is to safeguard people and their possessions from climatic elements, the insulating properties of the roof are a concern in its composition and the choice of roofing material.Some roof materials, those of natural fibrous materials specifically, such as thatch, have excellent insulating properties. For those that not, extra insulation is often installed under the outside level. In developed countries, nearly all dwellings have a ceiling installed under the structural members of the roof. The goal of a ceiling is to insulate against heat and cold, noise, dirt and often from the lice and droppings of wild birds who frequently choose roofs as nesting places.